Cables, connectors, and interconnects (cable assemblies) are essential yet often underappreciated parts of a system design. Even though the popular meme is “everything is going wireless” thus eliminating the need for cable assemblies, the reality is that these assemblies are critical both within circuits at either end of a wireless link, or as the only […]
RF power measurement, Part 2: What and how
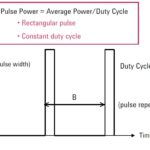
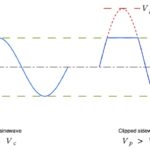
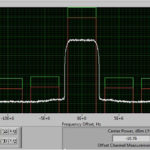
Part 1 of this FAQ introduced some of the basic issues related to the measurement of RF power, which is a primary parameter in most RF designs. Part 2 continues the discussion, looking at RF waveforms and sensors. Q: The term “power” is fairly broad; what are the specifics? A: There are actually several basic […]
Load lines, Part 2: The DC load line and AC operation
In Part 1 of this FAQ, we looked at the basic DC load line for a simple, basic common-emitter transistor configuration. Part 2 looks at how this graph is used to maintain the linear AC performance of the amplifier configuration. Note that the term “quiescent mode” or “quiescent state” is also used with ICs and […]
RF power measurement, Part 1: Why and where
When the subject is RF design, the word “power” dominates much of the discussion. This FAQ looks at some perspectives related to measurement of this vital RF parameter. Not only is power and measuring it among the most important RF design considerations, it is generally difficult to assess accurately, and it is getting harder […]
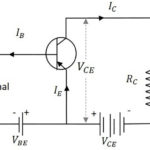
Load lines, Part 1: The basic transistor DC load line
There are concepts and terms in basic analog circuits which may not be familiar to designers who work primarily with digital circuits. Yet digital circuits are really specialized versions of analog ones, so these “old” analog principles play a large although somewhat invisible role. Part 1 of this FAQ discusses DC load-line basics, while Part […]
The RF power amplifier, Part 2: Considerations
Part 1 of this FAQ looked at the basic role and function of the RF power amplifier (PA). This part looks at some of the factors to consider when looking at possible PA devices. It is not a detailed run-through of the many parameters which characterize PAs, including many which are unique to the PA […]
DC power rails, Part 1: Basics and Designations
Most circuits and systems now run on DC-voltage power rails. That simple statement glosses over the wide range of voltages, issues of tolerance and ripple, designations of these rails, and management of both single and multiple rails. This FAQ will explore those uses. Q: Why are DC rails so important? A: They are the pathways […]
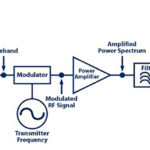
RF power amplifier, Part 1: Functions and Elements
In the RF signal chain, the power amplifier (PA) is the active element located between the transmitter signal chain circuitry and the antenna, Figure 1. It is often a single discrete component, one with requirements and parameters which differ from those of much of the transmit chain as well as the receiver circuitry. This FAQ […]
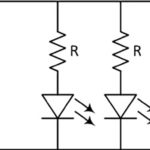
Driving LED arrays, Part 2: power
Part 1 of this FAQ looked at the basics of using LEDs in series, parallel, and series/parallel arrays, the implications on the power-sourcing requirements, and the impact of an LED failure. Part 2 looks at other practical issues associated with powering the array. Q: Given the various configurations, what sort of drive is “best” for […]
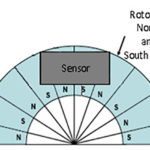
Rotary encoders, Part 2: magnetic encoders
Part 1 of this FAQ looked at the optical rotary encoder, a low-cost, high-resolution, easy-to-use sensor for indicating incremental shaft position (although it can be “upgraded” to indicate absolute position as well). Q: What is the basic principle of the magnetic encoder? A: The magnetic encoder uses a rotating gear made of ferrous metal and […]