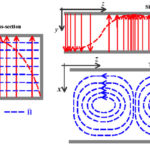
Waveguides confine and covey electromagnetic energy in the GHz+ range, just as coaxial cables do; they offer lower loss and other virtues, but at a cost in parts and ease of use. Waveguides (sometimes spelled out as wave guides) do not have the visibility or convenience of coaxial cables but they are an essential passive […]
FAQ
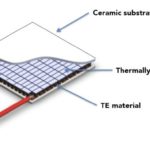
Keeping connected electronics cool with thermoelectric modules
Future connected vehicles are characterized by clusters of densely packed electronics. Thermoelectric modules can keep the temperature of these hot spots at manageable levels. Andrew Dereka | Laird Thermal Systems Advances in automotive electronics tend to come in small packages where dense circuitry squeezed into a pint-sized footprint generates lots of heat and thermal challenges […]
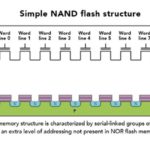
Flash memory keeps cars connected
A new kind of flash memory is optimized specifically to handle the hostile environment imposed on electronics in vehicular uses. Leland Teschler | Executive Editor You’d have to say the NAND flash memory had an inauspicious beginning. Invented in 1987 by Toshiba, the first NAND flash chip didn’t sell until 1995 when it finally found […]
Tech refresher: Basics of flash, NAND flash, and NOR flash
Flash memory stores information in an array of memory cells made from floating-gate transistors. Each memory cell resembles a standard metal-oxide-semiconductor field-effect transistor (MOSFET) except that the transistor has two gates instead of one. The floating gate (FG) and the control gate (CG) control the current flowing between the source and drain. The CG resembles […]
Data injection — Testing autonomous sensors through realistic simulation
Proof that autonomous vehicles are safe to put on the road begins with rigorous models of the sensors that guide them. Holger Krumm | dSPACE GmbH Onboard sensors are critical for autonomous vehicles to navigate the open road, but the real environment is full of obstacles. Everyday interferences such reflective surfaces, whiteout conditions, fog, rain, […]
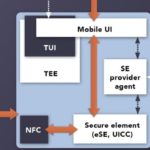
First implementations of Bluetooth-enabled keyless cars reveal a few bugs
The first production vehicle to employ a Bluetooth (actually a BLE) digital key is Tesla’s Model 3. When the owner approaches carrying his or her smartphone equipped with Bluetooth, Model 3s can be set to unlock their doors and trunk automatically, and starting the Model 3 is as simple as shifting out of Park. Nevertheless, […]
Spectrum co-existence challenges in the fully connected car
High-performance RF bandpass filters may hold the key to autonomous vehicle communication without interference. Ali Bawangaonwala | Qorvo, Inc. Continuing advances in technology are making the autonomous vehicle a practical reality, and there is frequent discussion among technologists about Wi-Fi and 5G as enablers of the connected car. Equally important, but less talked about, are […]
How GMR wheel speed sensors help advance vehicle control and braking systems
Giant magnetoresistance sensors are strong candidates for the high-accuracy wheel-speed sensing necessary in autonomous vehicle systems. Christine Graham | Allegro MicroSystems The purpose of a braking system has evolved from simplistic stopping to critical functions in vehicle safety through highly accurate feedback to traction control (TCS) and advanced driver assistance systems (ADAS). These advances have […]
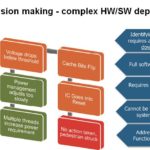
Validating correct behavior in ADAS and AV systems
Autonomous vehicles must operate in a world of uncertainties. Validation platforms are now capable of determining whether behavior is correct given complex contextual attributes. David Fritz, Mentor, A Siemens Business There is an interesting dashcam video circulating in the autonomous vehicle (AV) development community of a Tesla-paid test driver coming up on what the driver […]
Want a new perspective on battery management? Buy a plug-in EV.
One facet of EV ownership: Thinking of your daily commute power consumption as equivalent to the sunlight hitting 20 ft2 of your lawn. Rudye McGlothlin, Silicon Labs Earlier this year I took my first step into the EV future by buying a plug-in hybrid electric vehicle (PHEV) – a Chevrolet Volt. A unique car in […]