Most engineers are familiar with charge-coupled devices (CCDs) employed as image sensors. Pixels in a CCD sensor consist of P-doped metal-oxide semiconductor capacitors arranged in columns and rows to form an array. Light striking each pixel is converted to an electrical charge that varies according to the light intensity at that pixel. The CCD transfers […]
FAQ
Creating unique devices with haptic touch technology
Technology products are becoming increasingly difficult for designers and manufacturers to differentiate. Laptops, in particular, are all of a similar size and shape and offer the same functionality. Clamshell laptops typically combine the same three features – a display, a keyboard, and a touchpad – with few aspects that distinguish models […]
Basics of cooling transistors, IGBTs, and power FETs with heat sinks and PCBs
When designing any electronics that consume a significant amount of power, you need to consider where that power will go. With power electronics –such as IGBTs, power FETs, or power transistors – you might be expecting most of it to end up in your load, but there will be some which don’t. Even devices that […]
Top ten tips for nailing your PCB silkscreen design
By Suresh Patel, Sales Engineer,Mer-Mar Electronics Silkscreen represents the outer layers of a PCB that include text-based readable information such as component reference designator, test points, company logos, PCB part number and version number, etc. This is necessary for circuit board assembly, rework and debug support. The silkscreen ink is different from the regular printing […]
How can you detect hidden cameras invading your privacy?
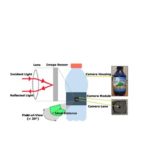
Using the time-of-flight (ToF) sensor on commodity smartphones, researchers at the National University of Singapore and Yonsei University have developed a technique to detect tiny hidden spy cameras concealed in privacy-invading locations, such as hotels and bathrooms. With small form factors and lens diameters as small as 1 to 2 millimeters, hidden cameras are difficult […]
How to measure display screen output
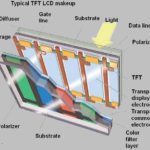
The flat display screens of today typically look great. But when it comes to quantifying their output, confusion may reign. There are three main measurement tools used to gage the output of displays. Before we get into their details, it might be helpful to review the main display technologies we are typically trying to measure. […]
Automobile Hands-Off Detection, Part 4: Capacitive solutions
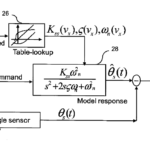
Cars with lane-keeping assistance (LKA) also are mandated to have a hands-off detection (HOD) function; there are several ways to meet this challenging requirement. Despite the BOM advantages of torque-based HOD, it has performance issues. Capacitive-based sensing is a viable alternative approach. Capacitive sensing for HOD monitors the driver’s grip on the steering wheel by […]
Automobile Hands-Off Detection, Part 3: Torque solutions
Cars with lane-keeping assistance (LKA) also are mandated to have a hands-off detection (HOD) function; there are several ways to meet this challenging requirement. The previous part of this article discussed the need for hands-off (or on) detection (HOD) and its connection to the lane-keeping assistance feature in today’s cars. This part will look at […]
Automobile Hands-Off Detection, Part 2: Requirements
Cars with lane-keeping assistance (LKA) also are mandated to have a hands-off detection (HOD) function; there are several ways to meet this challenging requirement. Where does “hands-off detection” (HOD) come into the picture? (Note: “hands-off detection” is sometimes spelled out as “hands-on detection;” fortunately, the acronym is the same either way.) It is a feature […]
Automobile Hands-Off Detection, Part 1: Basic issues
Cars with lane-keeping assistance (LKA) also are mandated to have a hands-off detection (HOD) function; there are several ways to meet this challenging requirement. Today’s cars are packed with all sorts of functions, features, and attributes that didn’t exist – or need to – just a few years ago. Whether for driver and passenger convenience, […]