By Margaret Bezerko, President of SensComp
When it comes to electronic design, function dictates framework. While piezoelectric, electrostatic, and electromagnetic devices offer distinct benefits, each comes with specific drawbacks and best-fit applications.
In this piece, we’ll examine each system with a quick analysis of operating mechanisms, potential pain points, and ideal use cases for current conditions.
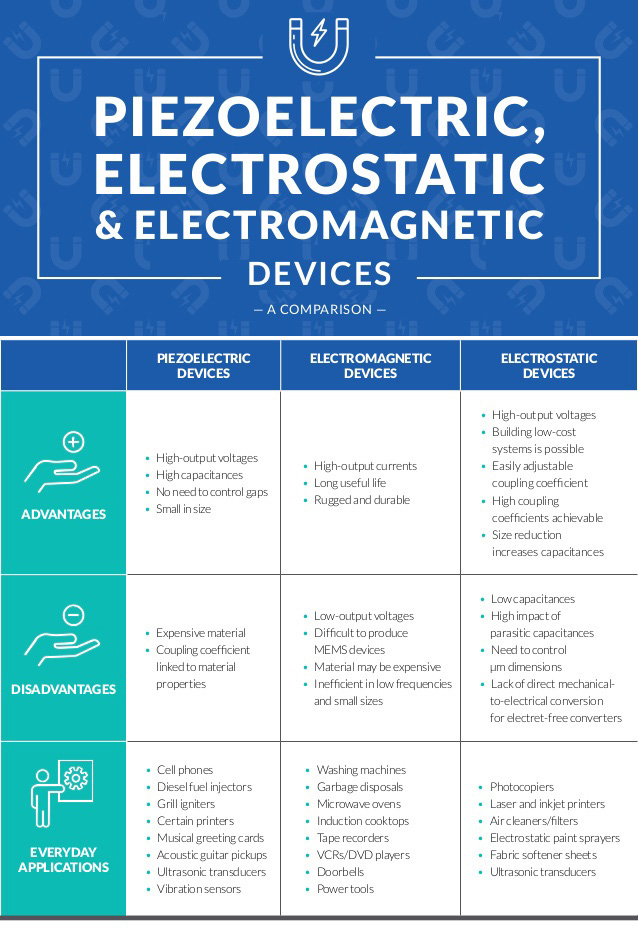
The piezoelectric potential
Piezoelectric devices leverage the ability of crystal structures to produce alternating current (AC) when exposed to mechanical stress. Simple piezoelectric devices typically use a crystal held between two metal plates. When the metal is placed under pressure or the device is subjected to sound waves, the crystal structure converts this mechanical force or audio pressure into a weak electric current. The effect also works in reverse: If an electric current is applied to the metal plates, the crystal will vibrate at the same wavelength.
With the ability to generate high-output voltages at high capacities and with no need to control gaps, these small form factor frameworks are ideally suited for use in sound-based devices such as mobile phones, microphones, vibration sensors and ultrasonic transducers.
Worth noting? They’re generally more expensive than electrostatic or electromagnetic options, and high-quality coupling materials are required to ensure sustained results.
The electrostatic solution
Electrostatic devices rely on the difference in charge between objects to store or conduct electricity. Consider the case of two oppositely charged objects, one large and one small. Their opposite charges cause them to actively attract, but the smaller object also contains a massive amount of potential (static) energy, which is equal to the amount of force required to remove it from its larger counterpart.
Like piezoelectric devices, electrostatic solutions can deliver high-output voltages. They can also be easily scaled up or down in size without a significant impact on their performance, and it’s possible to achieve high coupling coefficients across electrostatic applications. Their attract/repulse nature makes them ideal for use in photocopiers, air cleaners and filters, ultrasonic transducers, and even fabric softener sheets.
The caveat? Along with low comparative capacitances and the need to tightly control device dimensions, improper configuration of these devices can lead to potentially harmful and uncontrolled static energy discharges.
The electromagnetic mandate
Electromagnetic devices leverage the unique ability of magnetic metals such as iron to generate a magnetic field when electric current is applied. The most common form factor of electromagnetic devices consists of an electrically conductive material — typically copper — coiled around a larger piece of magnetic metal. When current is applied to the coil, the metal begins generating a magnetic field. The intensity of this field can be controlled by increasing or decreasing the current strength, and when the current stops flowing, the magnetic field also fades.
One of the biggest advantages offered by electromagnetic devices is durability. Unlike piezoelectric devices, which have the potential for shattered crystals, or electrostatic solutions with their required precise measurements, electromagnetic offerings can withstand high-volume, high-intensity use without suffering output or capacity loss. This makes them ideal for applications including washing machines, garbage disposals, induction cooktops, microwaves and power tools — any circumstance in which on-demand power and magnetism are required.
Three areas where electromagnetic efforts can’t stick the landing are voltage, cost and size. Compared to piezoelectric and electrostatic options, electromagnetic devices have low-output voltages, higher material costs and larger physical footprints, making them less than ideal for precision applications such as MEMS devices.
Positive outcomes
Selecting the ideal electric system depends on your use case. Need high-output voltages that support audio applications? Prioritize piezoelectric devices. For simple scaling with high coupling coefficients, embrace electrostatic solutions — and if you’re looking for durable, reliable output, make the move toward electromagnetic options.
About the author
Margaret Bezerko is President of SensComp, a world leader in ultrasonic sensors. She has 18 years of experience in the industry and currently focuses on leading the company in second-stage growth.