This continues the discussion on smart home technology basics. You can find part 1 here.
This continues the discussion on smart home technology basics. You can find part 1 here.
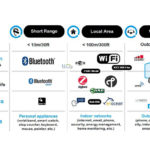
What is Z-Wave?
Behind the Z-Wave standard is the Z-Wave Alliance. It is a wireless protocol that will connect and control smart home and IoT devices today. Today, there are over 3400 certified Z-Wave smart home devices on the market. Current Z-Wave Alliance Board of Director companies supporting the technology include ADT, Alarm.com, Assa Abloy, LEEDARSON Group, Qolsys, Ring, Silicon Labs, and STRATIS.
The main characteristics of the technology are:
- It is a mesh network topology.
- The operating frequencies are 908 MHz and 916 MHz. Most wireless devices use the popular 4 GHz band. Because Z-Wave operates at lower frequencies, zero interference is possible.
- According to the Z-Wave Alliance, the devices should be situated around 30 feet apart for reliable communication with a maximum of 600 feet using mesh hopping to achieve optimal performance.
- The open-air transmission range is 328 feet (100 meters). With obstacles in the house, such as furniture, the more realistic distance is 80 feet.
- A maximum of 232 devices can be connected on one mesh network.
- Devices are backward and forward compatible.
- The technology requires a network hub. Compatible Hubs include the Wink Huband the SmartThings Hub.
What is Zigbee?
The Zigbee Alliance is the organization behind the Zigbee standard, which is backed by industry heavyweights such as Amazon, Apple, Comcast, Google, IKEA, NXP Semiconductors, Nordic Semiconductors, Schneider Electric, Silicon Labs, SmartThings (Samsung), Somfy, STMicroelectronics, Silicon Labs and, Texas Instruments. Today, the Alliance has 3400 certified products.
The main characteristics of the technology are:
- It utilizes a flexible, self-organizing mesh network topology.
- It operates on the IEEE802.15.4 radio frequency (2.4 GHz) and the Sub-GHz.
- The transmission speed is 250 kbps (over 4 GHz).
- The open-air transmission range is 984 feet (300 meters) line of sight. With obstacles in the house, such as furniture, the more realistic distance is 75 feet. The distance will increase with hopping.
- Theoretically, the technology can support up to 65,000 devices in a home environment.
- Zigbee devices operate in either hub, or hubless mode depends on the design.
What smart home platforms are available?
The smart home platforms available today include Amazon, Google, and Apple. More are expected to join in.
What are the future smart home development trends?
Smart home technology will continue to evolve to include more applications, features, and integration. The following are the five emerging trends that would impact smart home development.
- Z-Wave and Zigbee will lead smart home development for the foreseeable future. The other protocols will continue to own a niche in the market with some possible shakeout in the future. Wi-Fi and Bluetooth will remain part of the smart home landscape. They offer other wireless applications.
- New applications will be added. For example, finding lost keys and tracking an automobile’s whereabouts using IoT. Additionally, smart home healthcare implementation will be a growing sector within the smart home technology arena.
- Machine learning and AI integration will increase. Things will be able to communicate verbally with the users with high accuracy, with AI becoming part of the solutions. Additionally, AI will help users manage overall home operations, including energy management, security, and preventive maintenance.
- Smart building and smart home control will become more centralized. Builders will opt for smart control hubs which are centralized rather than scattered. The smart home technology will add a new dimension to the future home building segment. It will provide new features and additional revenue opportunities to home builders.
- User experience will be important. As suppliers offer more and more products to serve the smart home market, users will have more choices and become more selective. They will influence and eventually decide which technology and devices are user friendly. This will determine the success of future smart home devices.