Scientists have designed and constructed a prototype for a new solar cell that integrates multiple cells stacked into a single device capable of capturing nearly all of the energy in the solar spectrum. The new design converts direct sunlight to electricity with 44.5 percent efficiency, giving it the potential to become the most efficient solar cell in the world.
The approach is different from the solar panels one might commonly see on rooftops or in fields. The new device uses concentrator photovoltaic (CPV) panels that employ lenses to concentrate sunlight onto tiny, micro-scale solar cells. Because of their small size—less than one millimeter square—solar cells utilizing more sophisticated materials can be developed cost effectively.
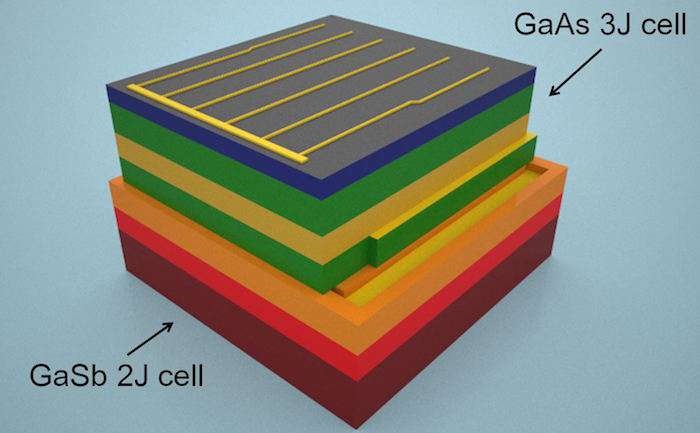
The stacked cell acts almost like a sieve for sunlight, with the specialized materials in each layer absorbing the energy of a specific set of wavelengths. By the time the light is funneled through the stack, just under half of the available energy has been converted into electricity. By comparison, the most common solar cell today converts only a quarter of the available energy into electricity.
“Around 99 percent of the power contained in direct sunlight reaching the surface of Earth falls between wavelengths of 250 nm and 2500 nm, but conventional materials for high-efficiency multi-junction solar cells cannot capture this entire spectral range,” said Matthew Lumb, lead author of the study and a research scientist at the GW School of Engineering and Applied Science. “Our new device is able to unlock the energy stored in the long-wavelength photons, which are lost in conventional solar cells, and therefore provides a pathway to realizing the ultimate multi-junction solar cell.”
While scientists have worked towards more efficient solar cells for years, this approach has two novel aspects. First, it uses a family of materials based on gallium antimonide (GaSb) substrates, which are usually found in applications for infra-red lasers and photodetectors. The novel GaSb-based solar cells are assembled into a stacked structure along with high efficiency solar cells grown on conventional substrates that capture shorter wavelength solar photons. In addition, the stacking procedure uses a technique known as transfer-printing, which enables three dimensional assembly of these tiny devices with a high degree of precision.
This particular solar cell is very expensive, however researchers believe it was important to show the upper limit of what is possible in terms of efficiency. Despite the current costs of the materials involved, the technique used to create the cells shows much promise. Eventually a similar product may be brought to market, enabled by cost reductions from very high solar concentration levels and technology to recycle the expensive growth substrates.
The study, “GaSb-based Solar Cells for Full Solar Spectrum Energy Harvesting,” was published in Advanced Energy Materials on Monday.

