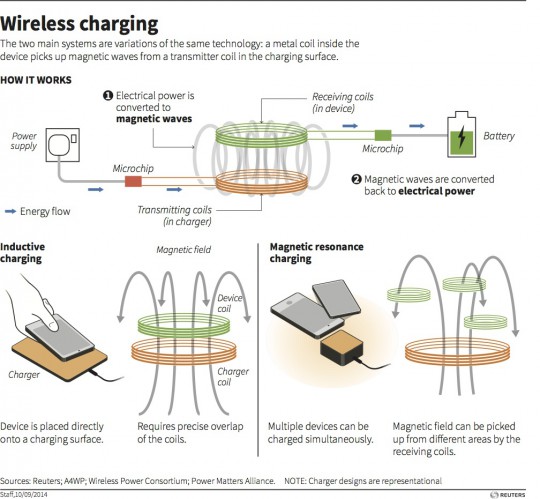
Despite being around for years, wireless charging is gaining mainstream industry appeal and taking significant steps towards perfection for the first time in recent memory. In a nutshell, wireless charging is the concept of powering electronics (smartphones, tablets, etc.) by only having direct physical contact with the charging station or pad (the power source). What most people don’t realize is there are two main methods of wireless charging known as inductive and magnetic resonance. Inductive charging utilizes an electromagnetic field for transferring energy between two objects through electromagnetic induction. Energy is sent through an inductive coupling to an electrical device, which can use that energy to charge batteries or run the device.
Resonance charging involves two copper coils, with one attached to a power source as the sending unit, and the other attached to the device that’s being charged (also referred to as the receiver). When objects of the same resonant frequency are placed close to each other, the energy produced is transferable between the pair. While it might not seem to be the case, there are some noteworthy distinctions between these two common methods of wireless charging. The infographic below provides a detailed visual to distinguish between the two wireless charging methods.