Researchers at Tohoku University have announced the development of a nonvolatile microcontroller unit (MCU) which achieves both high performance and ultra-low power by utilizing spintronics-based VLSI design technology.
The demand for low-power, high-performance microcontroller units (MCUs) has been increasing for power-supply-critical Internet-of-Things (IoT) sensor node applications. In sensor node applications, a distributed network of sensors extracts and gathers information, which is processed by MCUs and transmitted to a cloud-based data center. Various low-power MCUs for sensor node applications have been actively researched and developed, however, the required operation speed and signal processing throughput combined with low power consumption has not been achieved until now.
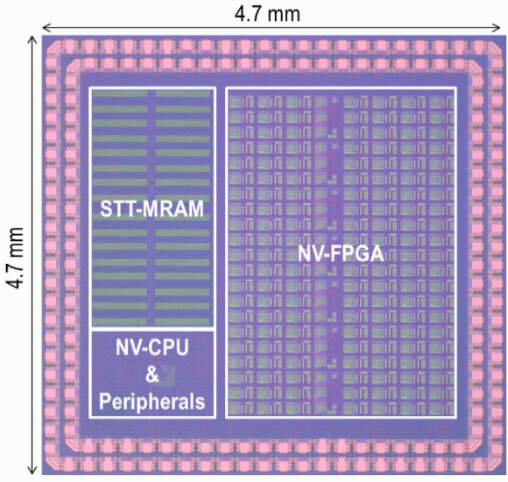
The research team led by Professors Tetsuo Endoh, Takahiro Hanyu and Associate Professor Masanori Natsui has developed an MCU using spintronics-based VLSI technology. In the newly developed spintronics-based MCU, all modules are made non-volatile using spintronics devices, and wasteful power consumption is entirely eliminated by controlling the power supply for each module independently.
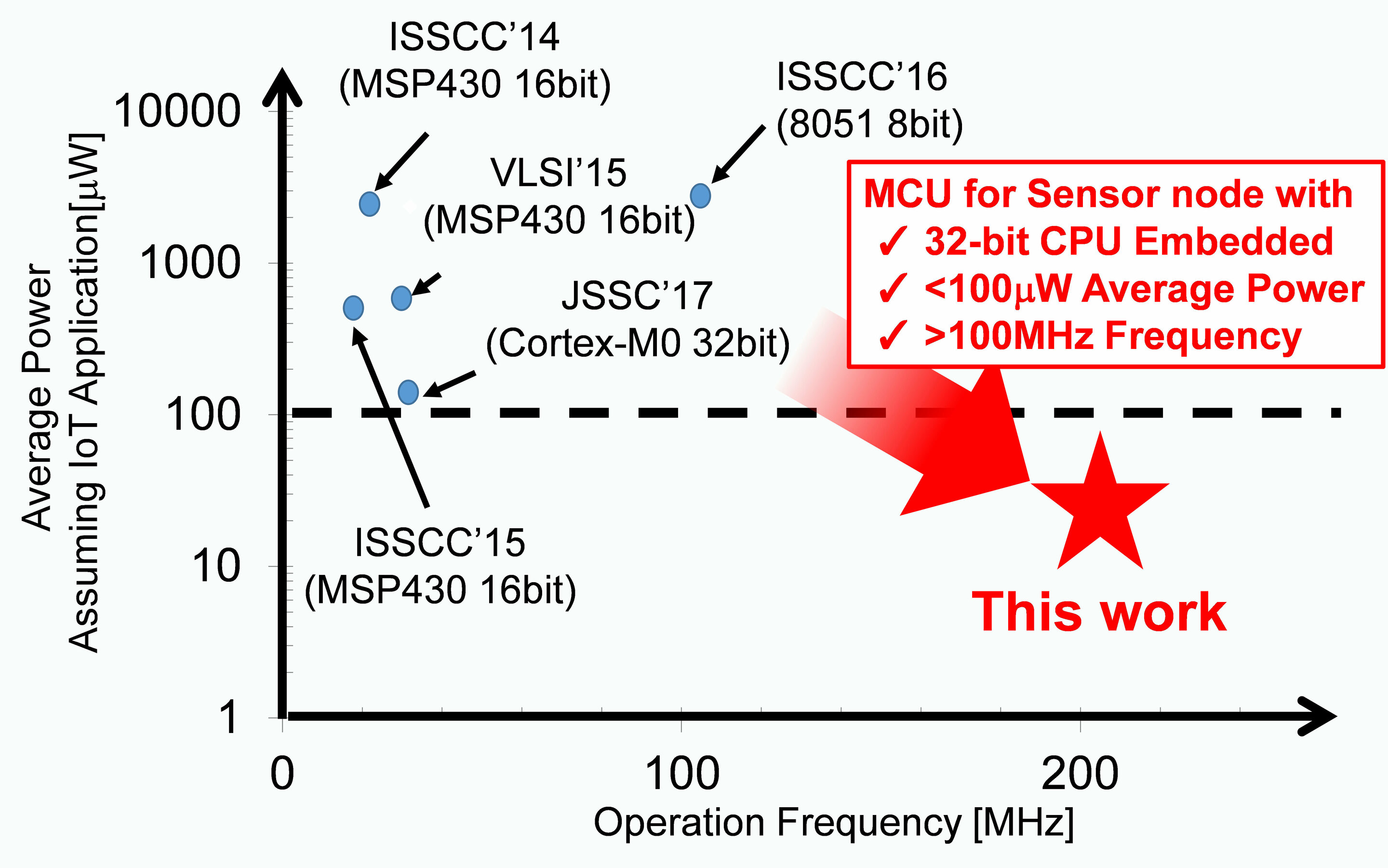
In addition, the data transfer bottleneck of logic and memory is relaxed by a memory controller that can speed up the entire system and a reconfigurable accelerator module is incorporated for executing application specific signal processing. These modifications enable the MCU to achieve ultra-low power consumption of 47.14μW at a high-speed operating frequency of 200MHz, which was confirmed from the measurement results of the fabricated chip.
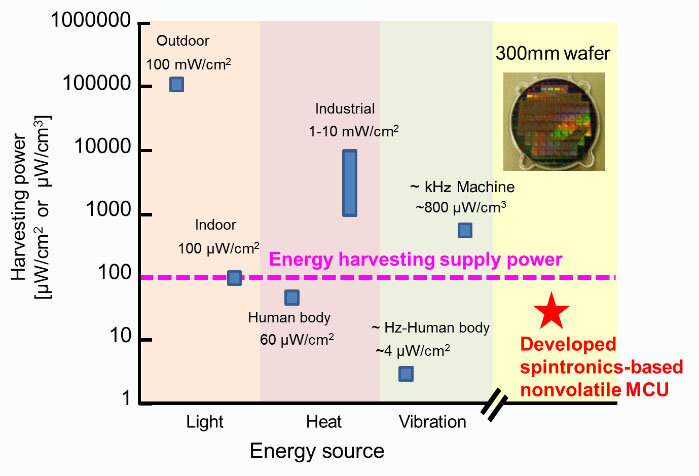
This MCU chip provides both the world’s highest processing performance and energy efficiency for highly functional IoT sensor nodes powered by harvested energy, which is derived from external sources such as solar power, thermal energy.
Results will be presented at 2019 IEEE International Solid-State Circuits Conference held in San Francisco, USA from February 17~21, 2019.

