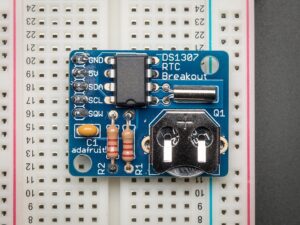
Figure 1: The DS1307 real time clock breakout board kit by Adafruit is an RTC with coin cell battery and will keep time for at least five years. Source: Adafruit.com
Microcontrollers act upon instructions a few bits at a time, collecting the next batch of bits at regular intervals. Those regular intervals need to have a regular cadence for the MCU to be predictable, so MCUs have at least one clock to keep timing going at a regular pace, much like you would use a metronome to keep pace in piano playing. Clocks can be internal or external, and come in many different types and implementations, but they all keep a regular drumbeat for the MCU. Clock frequency is often discussed with respect to the speed of an MCU or processor. A 32 mega Hertz (MHz) clock will cause the associated controller to complete 32 million (M) cycles per second (Hz), which is the same as 32 million instructions processed per second, if one full instruction is completed in each cycle.
“Overclocking” is sometimes discussed in reference to processors. Processors can be sped up by speeding up the clock, within certain limitations. Overclocking can cause problems if overdone. Modern processors are so fast that overclocking isn’t discussed as much anymore because it’s not worth the effort.
Another type of clock often mentioned in MCU datasheets, however, is the Real Time Clock (RTC). The RTC is a clock, but it’s the kind of clock that people use every day; an RTC is a 24-hour clock and/or a Julian calendar. RTCs are most often used when humans need an MCU to interact with them on their terms. Fitness bands all have RTCs because most people want to know when and how long an event occurred with respect to times that they can relate to. RTCs always need some kind of battery back-up, otherwise, like a night stand alarm clock without a 9V battery, when the power goes out in a thunderstorm, the alarm clock needs to be reset. When power goes out on an RTC, the RTC must be reset. The only alternative is to literally provide a battery back-up for the RTC, which is why many MCUs with an RTC will also have a coin cell battery.
Like quartz watches, RTCs need a clock signal or crystal oscillator to keep time. The most modern RTC solution uses a GPS receiver to tap time as kept by GPS satellites and does not need a battery backup as long as GPS satellites are available to send the current time so the RTC can set itself when power is restored.
The post FAQ: What’s the difference between a clock and a real time clock? appeared first on Microcontroller Tips.