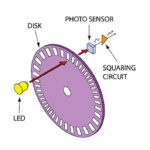
Across a wide range of applications, it is necessary to need to accurately sense the motion of a rotary shaft and know its position, speed, or even acceleration. To do this, a component called a shaft or rotary encoder is added to the motor/shaft assembly. (Note that the term “rotary encoder” is often shortened to […]
Driving LED arrays, Part 1: topologies
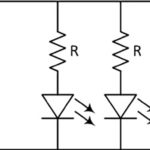
Light-emitting diodes – often referred to simply as LEDs – have become the preferred light source in many applications, whether for area illumination, spotlighting, signage, or backlighting. While there are some applications which prefer to use a smaller number of very high-power LEDs, many applications benefit from, or must use, a larger number of lower-to-moderate-power […]
Signal-channel diversity and fading, Part 2: Frequency Diversity
In Part 1 we looked at space diversity, which is the simplest form of signal-channel diversity. It has been used with success since the earliest days of wires and wired links, and it sees new uses in 5G MIMO and other advanced RF systems. We next look at the other very common form of signal-channel […]
Power-supply noise, Part 2: What is differential mode noise?
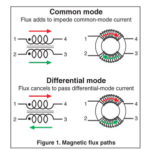
Part 1 looked at the basics of noise, especially concerning power supplies. There are two noise sources which are not as obvious to many engineers as noise that results from the switching action of the power supply: differential mode noise and common-mode noise. These two noise modes have different causes and thus different solutions Q: […]
Power-supply noise, Part 1
“Noise”—perhaps nothing worries design engineers as much as the implications of this single five-letter word. There are good reasons for this worry. Noise is often unpredictable; may come from internal and somewhat controllable sources, or external impossible-to-control sources; it can affect performance accuracy and consistency; it can cause products to not meet their target design […]
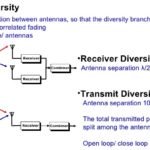
Signal-channel diversity and fading, Part 1: Space Diversity
In the engineering context, the phrase “channel diversity” refers to various techniques for getting a signal from point A to point B. The different approaches to diversity can be used individually or in combination. Q: What are the primary types of channel diversity in use? A: There are two primary types: space (spatial), and frequency. […]
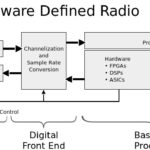
Radio receiver architectures, Part 2—Zero-IF and SDR
Part 1 of this FAQ looked at two basic receiver architectures: the tuned radio frequency approach (now largely obsolete due to performance shortcomings), and the superhet design which has been used with great success for about 100 years. Part 2 looks at two other architectures – the zero-IF design and the software-defined radio – which […]
Solar cells and power, Part 2 – power extraction
Part 1 looked at the solar cells themselves; Part 2 looks at how a cell or panel is managed for maximum performance. Q: How can the useful output of a solar cell or panel be maximized? A: While an active, in-use load or a power-generating facility could be connected directly to the output of a […]
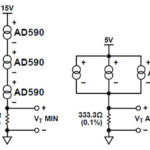
Solid-state temperature sensing, Part 2: application
In Part 1, we looked at the basic principle and function of the solid-state temperature sensors, as well as the first widely available model, the AD590. Part 2 looks at some application considerations. Q: What are the interface considerations? A: A basic solid-state sensor has a PTAT current-only output. This means that the subsequent circuitry, […]
Solar cells and power, Part 1 – basic operation
Both small- and large-scale solar power on is an effective way of generating electrical power from an impinging light source, usually the sun. Colloquially, the term may also encompass a local light source such as overhead illumination; thus this, a more-accurate broad term is photovoltaic (PV) power. Although the physics of the solar cell is […]